What is Reverse Logistics?
23 September 2024Unlike traditional logistics, where products flow from manufacturers to consumers, reverse logistics involves the movement of goods in the opposite direction—back from the end consumer towards any point along the supply chain.
According to Deloitte, by 2022, retailers are expected to handle approximately 13 billion returns worth around $573 billion annually. This highlights the significant impact of returns and the need for efficient reverse logistics processes.
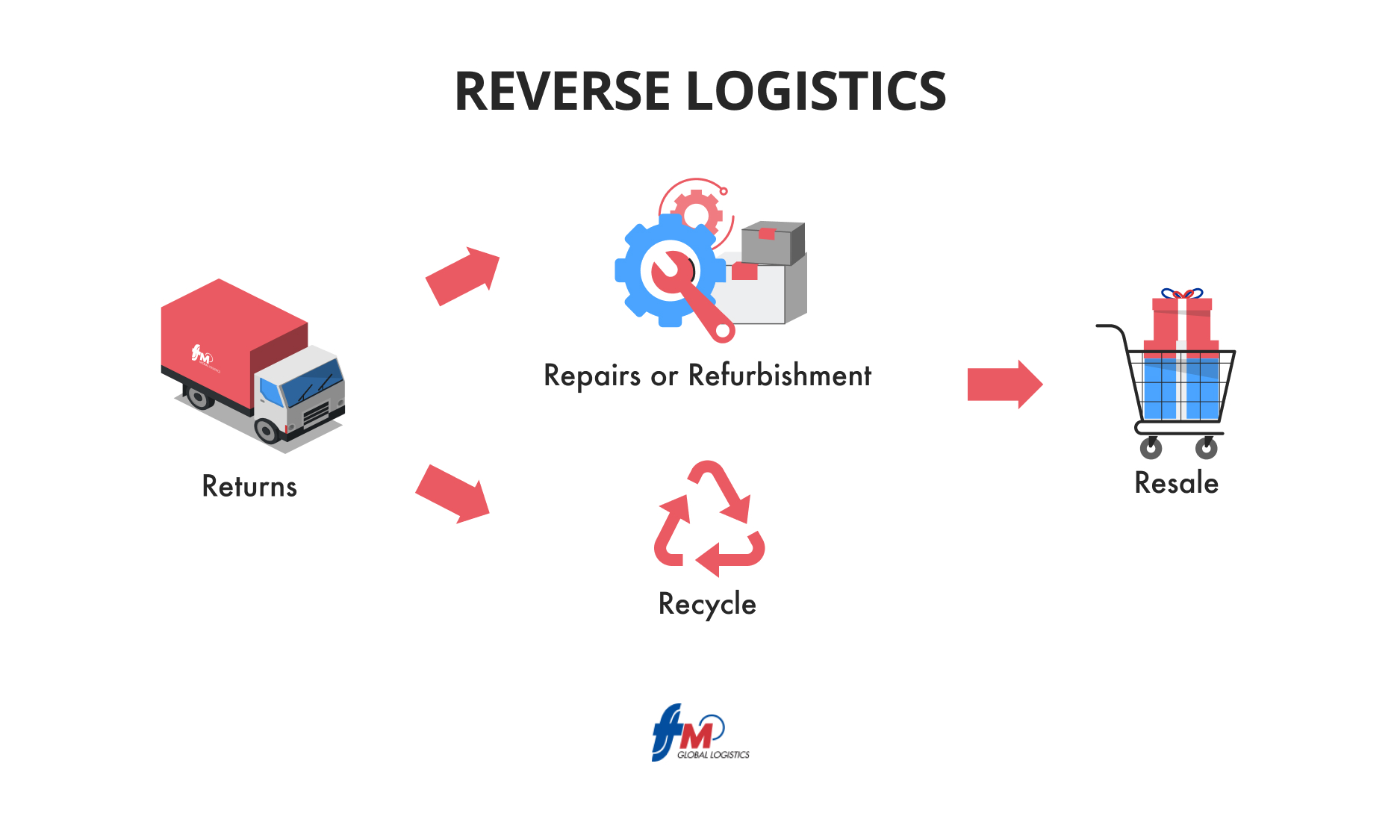
How does Reverse Logistics Work?
Traditionally, the product flow starts with suppliers, moving to factories or distributors, then to retailers, and finally to customers. However, reverse logistics flips this process on its head, requiring businesses to handle returns, repairs, recycling, and more. This reverse flow presents unique challenges, including setting up the right infrastructure and continually monitoring and evaluating the process to ensure effectiveness.
What Types of Reverse Logistics are There?
- Returns Management: Handling customer returns efficiently is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction. A seamless return process ensures that customers can easily return products and receive refunds or replacements.
- Return Policy and Procedure (RPP): A clear and consistent return policy helps manage customer expectations and streamline the return process. It should be regularly reviewed and updated to align with changing business needs and customer preferences.
- Remanufacturing or Refurbishment: This involves repairing and rebuilding products or recovering parts from defective items for reuse. Refurbished products can be resold, extending their lifecycle and adding value.
- Packaging Management: Reusing and repairing packaging materials can reduce waste and lower costs. Proper packaging management also helps ensure that products are protected during return shipments.
- End-of-Life (EOL) Management: Products at the end of their useful life must be returned for proper disposal or recycling. This ensures that materials are managed sustainably and in compliance with environmental regulations.
- Delivery Failure: Products that cannot be delivered are returned to fulfillment centers and may be redirected or sent back to the manufacturer. Efficient handling of delivery failures helps minimize disruptions and costs.
- Rentals and Leasing: Rented or leased products must be returned at the end of their term. These items are then processed for either disposal, recycling, or redeployment.
- Repairs and Maintenance: For products needing repairs, such as consumer electronics, reverse logistics ensures that these items are returned, repaired, and either sent back to the customer or resold.
What are the Key Steps in Reverse Logistics?
- Processing the Return: The journey begins when a customer initiates a return. This step involves scheduling return shipments, approving refunds, and organizing replacements if necessary. It’s also beneficial to ask customers for feedback on why they are returning the product.
- Dealing with Returns: Upon receiving the returned product, it must be inspected to determine its condition. Will the product require cleaning, repairs, or replacing of parts? Categorizing returned products into “refurbish,” “recycle,” and “repair” helps to streamline the reverse logistics process and ensures each item is handled appropriately.
- Recycling and Repairing: Recycled products should be stripped of reusable parts and broken down into raw materials for reuse. Meanwhile, items needing repair should be fixed and either returned to the customer or disposed of if irreparable.
- Moving Products: It’s important to keep products in motion to reduce the amount of waste produced when products are left in limbo for long periods of time. Once moved and properly managed, products can continue on in their journey through the supply chain, whether it be back to the manufacturer or back to the customer.
Benefits of Effective Reverse Logistics
- Cost Reduction: Efficient handling of returns and recycling can lower operational costs.
- Greater Customer Satisfaction: A smooth return process enhances customer experience and loyalty.
- Improved Brand Sentiment: Effective reverse logistics helps build a positive brand image.
- Waste Reduction and Sustainability: Responsible recycling and refurbishment practices contribute to environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
By understanding and implementing reverse logistics, businesses can achieve a more efficient and sustainable supply chain, ultimately leading to better service, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.



